Privacy Policy for http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/
If you require any more information or have any questions about our privacy policy, please feel free to contact us by email at ism4il89@gmail.com.
At http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/, the privacy of our visitors is of extreme importance to us. This privacy policy document outlines the types of personal information is received and collected by http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/ and how it is used.
Log Files
Like many other Web sites, http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/ makes use of log files. The information inside the log files includes internet protocol ( IP ) addresses, type of browser, Internet Service Provider ( ISP ), date/time stamp, referring/exit pages, and number of clicks to analyze trends, administer the site, track user’s movement around the site, and gather demographic information. IP addresses, and other such information are not linked to any information that is personally identifiable.
Cookies and Web Beacons
http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/ does use cookies to store information about visitors preferences, record user-specific information on which pages the user access or visit, customize Web page content based on visitors browser type or other information that the visitor sends via their browser.
DoubleClick DART Cookie
.:: Google, as a third party vendor, uses cookies to serve ads on http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/.
.:: Google's use of the DART cookie enables it to serve ads to users based on their visit to http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/ and other sites on the Internet.
.:: Users may opt out of the use of the DART cookie by visiting the Google ad and content network privacy policy at the following URL - http://www.google.com/privacy_ads.html
Some of our advertising partners may use cookies and web beacons on our site. Our advertising partners include ....
Google Adsense
These third-party ad servers or ad networks use technology to the advertisements and links that appear on http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/ send directly to your browsers. They automatically receive your IP address when this occurs. Other technologies ( such as cookies, JavaScript, or Web Beacons ) may also be used by the third-party ad networks to measure the effectiveness of their advertisements and / or to personalize the advertising content that you see.
http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/ has no access to or control over these cookies that are used by third-party advertisers.
You should consult the respective privacy policies of these third-party ad servers for more detailed information on their practices as well as for instructions about how to opt-out of certain practices. http://performanceaccounting.blogspot.com/'s privacy policy does not apply to, and we cannot control the activities of, such other advertisers or web sites.
If you wish to disable cookies, you may do so through your individual browser options. More detailed information about cookie management with specific web browsers can be found at the browsers' respective websites.
Sunday, August 14, 2011
EVOLUTION AND MEANING OF ACCOUNTING

There are many evidences of keeping records back in 3000 BC. But, systematic book keeping was only found sometimes in the 14th Century. The first record of a complete accounting was found in the records of Geneo, Italy. The first published work describing accounting was one of the five sections in Summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportion et Proportionality (everything about Arithmetic, Geometry and Proportion) published by Luca Pacioli in1494 in Venice. This section of accounting was the world's only accounting textbook until the 16th century. Luca Pacioli is known as the "Father of Accounting". He introduced Double Entry System in 1494 in Italy.
Meaning
Accounting is the process of recording business transactions in systematic way in terms of money, reporting results of business activities and interpreting such results for the purpose of effective control of future activities. It includes identifying, recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing and interpreting financial transactions.
Meaning
Accounting is the process of recording business transactions in systematic way in terms of money, reporting results of business activities and interpreting such results for the purpose of effective control of future activities. It includes identifying, recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing and interpreting financial transactions.
Characteristics of Accounting

The following are the characteristics of accounting:
1. In accounting system, only those transactions which are related to money are recorded in the books of accounts. Non-monetary transactions like strikes are not recorded in the books of accounts.
2. Accounting is an art of recording business transactions in the books of accounts maintained as per specific rules and principles.
3. In accounting process, those transactions relating to particular nature are recorded in separate accounts, so it is a process of classifying business transactions.
4. Accounting is an art of summarizing all business transactions as it includes the act of balancing ledger accounts, preparing trial balance and finally final accounts.
5. Accounting includes analyzing and interpreting the financial data to compare such results with that of previous years.
1. In accounting system, only those transactions which are related to money are recorded in the books of accounts. Non-monetary transactions like strikes are not recorded in the books of accounts.
2. Accounting is an art of recording business transactions in the books of accounts maintained as per specific rules and principles.
3. In accounting process, those transactions relating to particular nature are recorded in separate accounts, so it is a process of classifying business transactions.
4. Accounting is an art of summarizing all business transactions as it includes the act of balancing ledger accounts, preparing trial balance and finally final accounts.
5. Accounting includes analyzing and interpreting the financial data to compare such results with that of previous years.
Importance of Accounting

1.Importance to trading concern- Business is very competitive nowadays. Business cannot operate on sound basis for a long time until the financial records are kept and made available to its users. Accounting helps to determine profit or loss of the business. It also gives knowledge of debtors, creditors, other assets and liabilities.
2.Importance to non-trading concerns- Although the non- trading concerns are established with service motive, accounting is equally importance to them as they have to carry out their works within their funds and also their operations have to be answerable to the board of governors. They need to prepare balance sheet to know the financial position of their business.
3.Importance to the professionals and individuals- Professionals such as contractors, engineers, lawyers,etc. maintain accounting books to know their surplus or deficit of
incomes and expenditures of a particular period. Accounting also help farmers, workers and politicians to record their sources and uses of funds. It helps them to make expenditures within the limitation of budget.
4. Importance to the government- Accounting also helps to record the expenditures and revenues of the government. Every government should maintain a large number of accounting forms and books such as budget sheet, cash book, statement of expenditure,etc. With the help of accounting information the government plans for future budget. Accounting can be provided as documentary proof of the activities carried by a government, so it acts as a memory centre.
Principles of Accounting

The following are the principles of accounting:
1. Principle of business entity- In accounting every business organization is treated as a separate body from its owner. Business are perceived treated as separate entities and the purpose of accounting is to record its transactions and report its financial position and profitability.Transactions of owners are not recorded in the business.
2. Principle of money measurement- The transactions are measured, recorded and reported
in terms of monetary value which is known as money management principle. Expression of all assets and liabilities in terms of money creates common measure that permits addition and subtraction of all forms of assets and liabilities and makes possible the
preparation of financial statements.
3. Principle of accounting period- The life of the business is perpetual but it has to report the results of the activities conducted in specific period. Generally, one year is taken as an accounting period.
4. Cost principle- Cost principle states that all the transactions should be recorded at their monetary cost of acquisition. Assets and liabilities are recorded in the books of accounts at the acquisition and are carried from year to year at acquisition cost,irrespective of any subsequent increase or decrease in their market value.
5. Realization principle- According to this principle, revenue is measured by amount charged for goods sold or services rendered to the customers. It states that revenue should be recognized in the period when sale is made and specifies that revenues should be measured as cash received and cash equivalent of other item received.
6. Objectivity principle- This principle states that accounting data should be verifiable. It means that accounts which are prepared should be capable of independent verification.
7. Matching concept- In it, all the expenses incurred in generating revenue should be identified or matched with the revenue generated, period by period. This concept attempts to charge to an accounting period only those expenses which are consumed during the period.
1. Principle of business entity- In accounting every business organization is treated as a separate body from its owner. Business are perceived treated as separate entities and the purpose of accounting is to record its transactions and report its financial position and profitability.Transactions of owners are not recorded in the business.
2. Principle of money measurement- The transactions are measured, recorded and reported
in terms of monetary value which is known as money management principle. Expression of all assets and liabilities in terms of money creates common measure that permits addition and subtraction of all forms of assets and liabilities and makes possible the
preparation of financial statements.
3. Principle of accounting period- The life of the business is perpetual but it has to report the results of the activities conducted in specific period. Generally, one year is taken as an accounting period.
4. Cost principle- Cost principle states that all the transactions should be recorded at their monetary cost of acquisition. Assets and liabilities are recorded in the books of accounts at the acquisition and are carried from year to year at acquisition cost,irrespective of any subsequent increase or decrease in their market value.
5. Realization principle- According to this principle, revenue is measured by amount charged for goods sold or services rendered to the customers. It states that revenue should be recognized in the period when sale is made and specifies that revenues should be measured as cash received and cash equivalent of other item received.
6. Objectivity principle- This principle states that accounting data should be verifiable. It means that accounts which are prepared should be capable of independent verification.
7. Matching concept- In it, all the expenses incurred in generating revenue should be identified or matched with the revenue generated, period by period. This concept attempts to charge to an accounting period only those expenses which are consumed during the period.
Accounting Process

Following processes are followed in the accounting :
1. Identification of financial transactions: In accounting, only those transactions which are of financial nature are recorded in the books of accounts. If a transaction do not have financial character then such transactions are not recorded.
2. Recording of financial transactions: In accounting, financial transactions are recorded in systematic way in a book called "journal." This book is further sub-divided into various subsidiary books such as Cash Book, Purchase Book, Sales Book, Purchase Return Book and Sales Return Book.
3. Classifying of financial transactions: There may be thousands of records and it may be troublesome to find out details about a particular transaction. So, for the easy location of the transaction, the transactions of same nature are grouped into one place by opening accounts in a book called "ledger."
4. Summarizing: The classified information may be large in number and the users of accounting information may not have time to go through all the records. So, for presenting the data in concise manner, summarizing is done. It includes preparation of trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet.
5. Communicating: The processed information have to be communicated to those people who have to make the use of them like owners, managers, creditors,etc. Communicating is done through an annual report.
1. Identification of financial transactions: In accounting, only those transactions which are of financial nature are recorded in the books of accounts. If a transaction do not have financial character then such transactions are not recorded.
2. Recording of financial transactions: In accounting, financial transactions are recorded in systematic way in a book called "journal." This book is further sub-divided into various subsidiary books such as Cash Book, Purchase Book, Sales Book, Purchase Return Book and Sales Return Book.
3. Classifying of financial transactions: There may be thousands of records and it may be troublesome to find out details about a particular transaction. So, for the easy location of the transaction, the transactions of same nature are grouped into one place by opening accounts in a book called "ledger."
4. Summarizing: The classified information may be large in number and the users of accounting information may not have time to go through all the records. So, for presenting the data in concise manner, summarizing is done. It includes preparation of trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet.
5. Communicating: The processed information have to be communicated to those people who have to make the use of them like owners, managers, creditors,etc. Communicating is done through an annual report.
Government and Commercial Accounting

Government Accounting- Government accounting is the accounting used by government offices to keep the record of revenue and expenditures of government. It provides necessary information and data to the government for various activities and it helps to control over budget and fix the responsibility. It is maintained on cash basis. It provides information about the services rendered to the public by utilizing public funds and properties. In it, the financial operations are governed by legal provisions. The main purpose of it is to reflect the plans and policies of the government in financial terms.It is prepared for the consumption of government offices and general public.It is maintained on the basis of government budget.
Commercial Accounting- Commercial Accounting is the accounting used by business firm to calculate the amount of profit or loss made during a period. In it, outstanding expenses and accrued expenses are also considered. Government is not responsible in any financial activity and financial activities are not governed by the legal government. It is maintained for the consumption of owner of enterprises. The main purpose of it is to find the profit earned or loss suffered during a financial year
Accounting Equation

The assets,liabilities and capital are the backbones of modern day accounting. The relationship that they share can be expressed using the basic accounting equation. It is the mathematical form of explaining double entry system of book keeping according to which, the total assets being always equal to the total equities consisting of the capital and liabilities. The organization is represented by assets, which are the things owned by it and available for use in carrying on work of that organization. Creditors' claims for having sold, provided or loaned assets or services by them to the organization with the payments by the organization to be made in the future are represented by the liabilities. The capital represents the organization's claim against the assets after the liabilities have been subtracted.
It is expressed as:
Assets = Liability + Capital
For example: When the resources are supplied by persons other than the owner, these persons are known as liabilities, then the equation will be:-
Resources in business = Resources supplied by the owner + Resources supplied by the outsiders.
Assets=Capital+Liabilities
The twos sides of the equation are always equal, because both sides deal with the same thing but form a different viewpoint.
Resources in business(what they are)= Resources in business(who supplied them)
Introduction and meaning of Book Keeping

Introduction of book keeping
Book keeping is that branch of knowledge, which tells us how to keep the record of financial transactions in a systematic manner. Each business deals a number of financial transactions daily, which can be expressed in monetary value. In order to find out the profit or loss of the business, it is essential to keep a complete and systematic record of these business transactions. The necessity of book keeping arose mainly due to the fact that memory of the human beings is limited. A person may fail to recall all the transactions, in the absence of written records, he had done. A person must maintain a note or diary in which details of the transactions have been recorded. The fundamental idea behind this record is to show a correct position relating to income and expenditures.
Meaning of book keeping
Book keeping refers to the recording of economic events. It usually involves only the recording of economic events (transactions) and so it is just one phase of the accounting process. It is a recording phase of accounting and involves journalizing,
posting into ledger accounts and balancing and closing of ledger accounts. It is only a part of accounting. It is the science and art of recording transactions in money's worth so accurately and systematically, in a certain set of books, that the true state of businessman's affairs can be correctly ascertained.
Advantages of Double Entry Book Keeping System

The following are the advantages of double entry book keeping system:
1. Complete records of each transaction- It keeps the records of personal accounts relating to debtors and creditors as well as impersonal accounts relating to goods, profits, losses,etc. Thus, all the information regarding purchases, sales, expenses, incomes, profits, losses, debtors, creditors, etc. are available in this system.
2. Checking of arithmetical accuracy- Under this system, there is every debit amount for a credit amount, as a result, the total of all debits and all credits is equal. It can be tested by the preparation of trial balance from the ledger
balances. It helps to prevent frauds and manipulations.
3. Result of business- Since it keeps a complete records of business transactions, it is possible to determine the net profit earned or net loss suffered by the preparation of profit and loss account and income and expenditure account during the year.
4. Knowledge of financial position- It helps to know about the capital, liabilities and assets of a firm with the help of balance sheet prepared immediately after trading and profit and loss accounts. Moreover, it also helps to ascertain the amount of debtors and creditors.
1. Complete records of each transaction- It keeps the records of personal accounts relating to debtors and creditors as well as impersonal accounts relating to goods, profits, losses,etc. Thus, all the information regarding purchases, sales, expenses, incomes, profits, losses, debtors, creditors, etc. are available in this system.
2. Checking of arithmetical accuracy- Under this system, there is every debit amount for a credit amount, as a result, the total of all debits and all credits is equal. It can be tested by the preparation of trial balance from the ledger
balances. It helps to prevent frauds and manipulations.
3. Result of business- Since it keeps a complete records of business transactions, it is possible to determine the net profit earned or net loss suffered by the preparation of profit and loss account and income and expenditure account during the year.
4. Knowledge of financial position- It helps to know about the capital, liabilities and assets of a firm with the help of balance sheet prepared immediately after trading and profit and loss accounts. Moreover, it also helps to ascertain the amount of debtors and creditors.
Meaning and Features of Single Entry Book keeping System

Meaning of Single Entry Book Keeping System
Under single entry book keeping system, only one aspect of a transaction is recorded, so it is known as incomplete system of recording transactions. Under it only records of cash and personal accounts are maintained. In it, accounts relating to debtors , creditors and cash are prepared. It ignores all impersonal account like salaries, wages, sales, purchases,etc. It maintains a cash book and personal accounts but does not record nominal and real accounts. It is not a reliable system but it is still used by small organizations to keep the records of transactions.
Features of Single Entry Book Keeping System
1. It maintains only accounts relating to person but it ignores the real and nominal accounts.
2. It prepares the cash book but both personal and business cash transactions are recorded in the same book.
3. It is suitable to small traders having lesser numbers having lesser number of transactions.
4. It lacks the specific rules of maintaining books of accounts as a result there is no uniformity in accounts of
different firms.
5. Trial balance cannot be prepared under this system.
6. The profit or loss calculated under this system is only a guess.
Under single entry book keeping system, only one aspect of a transaction is recorded, so it is known as incomplete system of recording transactions. Under it only records of cash and personal accounts are maintained. In it, accounts relating to debtors , creditors and cash are prepared. It ignores all impersonal account like salaries, wages, sales, purchases,etc. It maintains a cash book and personal accounts but does not record nominal and real accounts. It is not a reliable system but it is still used by small organizations to keep the records of transactions.
Features of Single Entry Book Keeping System
1. It maintains only accounts relating to person but it ignores the real and nominal accounts.
2. It prepares the cash book but both personal and business cash transactions are recorded in the same book.
3. It is suitable to small traders having lesser numbers having lesser number of transactions.
4. It lacks the specific rules of maintaining books of accounts as a result there is no uniformity in accounts of
different firms.
5. Trial balance cannot be prepared under this system.
6. The profit or loss calculated under this system is only a guess.
Books of original entry

Journal
Journal is a book which records every financial transaction of business organization. The financial transactions are firstly recorded into journal in chronological order. It is known as "Book of original entry ." Journal is a book of prime or original entry in which all the transactions pf a business are systematically recorded according to their dates of occurrence and is maintained with a view to help prepare the subsequent ledger book.
Journal is derived from the word 'jour' which means a diary or long book i.e. daily books. Journal can be defined as a book which records financial transactions of each day based on the principle of double entry book keeping.
According to R.N. Carter, 'The journal' or 'daily record' as originally used was a book of prime entry inn which transactions were copied in order of date from a memorandum or waste book. The
entries as they were copied, were classified into debits and credits, so as to facilities their beings correctly posted afterward in the ledger.'
Journal is a book which records every financial transaction of business organization. The financial transactions are firstly recorded into journal in chronological order. It is known as "Book of original entry ." Journal is a book of prime or original entry in which all the transactions pf a business are systematically recorded according to their dates of occurrence and is maintained with a view to help prepare the subsequent ledger book.
Journal is derived from the word 'jour' which means a diary or long book i.e. daily books. Journal can be defined as a book which records financial transactions of each day based on the principle of double entry book keeping.
According to R.N. Carter, 'The journal' or 'daily record' as originally used was a book of prime entry inn which transactions were copied in order of date from a memorandum or waste book. The
entries as they were copied, were classified into debits and credits, so as to facilities their beings correctly posted afterward in the ledger.'
Objectives and Types of Journal
The objectives of journal are :-
1. To record the financial transactions in a systematic way.
2. To show necessary information of the transactions.
3. To provide legal evidences of business.
4. To provide date wise record of transactions.
5. To help in the preparation of ledger accounts.
The types of journal are:-
1. General Journal
2. Special Journal
General journal records all types of business transactions in systematic,scientific and sequential order. It is used when the nonmember of transaction is limited and manageable in a single book. Normally, the term 'journal' is referred as general journal.
On the other hand, in large organization , it may not be possible to record the transactions as
and when they occur because of voluminous transactions. Therefore, these business houses divide journal into several division depending upon the need. For example, purchase book is maintained for the goods purchased on credit, sales book is maintained for the goods sold on credit, cash book is used for recording cash and banking transactions and so on. Thus, journal is divided into several books requiring separate persons. Such books as Purchase Book, Cash Book, etc. are called special journal.
1. To record the financial transactions in a systematic way.
2. To show necessary information of the transactions.
3. To provide legal evidences of business.
4. To provide date wise record of transactions.
5. To help in the preparation of ledger accounts.
The types of journal are:-
1. General Journal
2. Special Journal
General journal records all types of business transactions in systematic,scientific and sequential order. It is used when the nonmember of transaction is limited and manageable in a single book. Normally, the term 'journal' is referred as general journal.
On the other hand, in large organization , it may not be possible to record the transactions as
and when they occur because of voluminous transactions. Therefore, these business houses divide journal into several division depending upon the need. For example, purchase book is maintained for the goods purchased on credit, sales book is maintained for the goods sold on credit, cash book is used for recording cash and banking transactions and so on. Thus, journal is divided into several books requiring separate persons. Such books as Purchase Book, Cash Book, etc. are called special journal.
Journalising and rules of journalising
Journalising
Journalising is a systematic process of recording financial transaction. Such recording are made in terms of debit and credit. In it, financial transactions are recorded in the original book.
Rules of journalising
Every financial transaction of a business organization has dual effect.It means that every financial transaction of a business involves at least two accounts. One account is debited and the other account is credited.
Before journalising a transaction, following three steps must be borne in mind.
1. Firstly, we need to find out the two aspects or two fold effects of a transaction.
2. Secondly, we need to identify the accounts whether they are personal, real or nominal accounts.
3. Finally, we need to use the rules of debit and credit.
There are two concept available for recording financial transactions of business organization. They are:- Traditional concepts and moder concept. Traditional concept of journalising is also known as British Approach and modern concept of journalising is also known as American Approach.
Traditional concept of recording financial transactions

There are two concepts available for recording financial transactions. They are:
1. Traditional concepts
2. Modern concepts
Traditional concepts- Under this concept, transactions are recorded by classifying accounts into three accounts which are personal accounts, real accounts and nominal accounts. In personal accounts, the transactions relating to persons, firms, organization, etc. are recorded. It's examples are Ram account, debtor's account, creditor's account, Himalayan co. ltd account,etc. The rules of debit and credit for it are
debit: the receiver and credit: the giver.
In real accounts, transactions relating to assets or properties are recorded. It's examples are machinery account, goodwill account, furniture account, Cash account, Bank account, etc. The rules of debit and credit for it are
debit: what comes in and credit: what goes out.
In nominal accounts, transactions relating to expenses, incomes, losses or gains are recorded.It's examples are salary account, rent account, commission account, Wages account, etc.The rules of debit and credit for this account are
debit: all expenditures and losses and credit: all incomes and gains.
Modern concept of recording financial transactions

Modern concept of recording financial transactions
Under this concept, any increase or decrease in assets, liabilities, capital, revenue, expenses or losses is examined.
Assets are the properties of the business organization which are not for resale purpose. It includes cash, plant and machinery, land and building,etc.
Liabilities are the economic obligations of business firm that have been incurred as a result of transaction which can be measured in monetary term. It includes loans, debentures,bills payable, creditors,etc.
Capital is the amount invested in a business by the proprietor. It is considered as a liability.
Revenue is the amount received from customers for the transfer of goods or services regularly during a period of time.It includes the amount received from the sale of trading goods, rent, commission, interest,etc.
Expenses are those costs, which are incurred to produce and sell goods or services like purchase of material, payment of salary, etc. Loss is occurred when expenses exceed the incomes.
The rules of debit and credit for the five types of transactions are:
Increase in assets: debited and decrease in assets: credited
Increase in liability: credited and decrease in liability: debited
Increase in capital: credited and decrease in capital: debited
Increase in revenue: credited and decrease in revenue: debited
Increase in expenses or losses: debited and decrease in expenses or losses: credited
Under this concept, any increase or decrease in assets, liabilities, capital, revenue, expenses or losses is examined.
Assets are the properties of the business organization which are not for resale purpose. It includes cash, plant and machinery, land and building,etc.
Liabilities are the economic obligations of business firm that have been incurred as a result of transaction which can be measured in monetary term. It includes loans, debentures,bills payable, creditors,etc.
Capital is the amount invested in a business by the proprietor. It is considered as a liability.
Revenue is the amount received from customers for the transfer of goods or services regularly during a period of time.It includes the amount received from the sale of trading goods, rent, commission, interest,etc.
Expenses are those costs, which are incurred to produce and sell goods or services like purchase of material, payment of salary, etc. Loss is occurred when expenses exceed the incomes.
The rules of debit and credit for the five types of transactions are:
Increase in assets: debited and decrease in assets: credited
Increase in liability: credited and decrease in liability: debited
Increase in capital: credited and decrease in capital: debited
Increase in revenue: credited and decrease in revenue: debited
Increase in expenses or losses: debited and decrease in expenses or losses: credited
Ledger
Introduction and meaning
The records of transactions in the journal may run into thousands of pages and it may be difficult to find out the details about a particular transaction. It doesnot provide the information about the details about the position of a particular account. So, to find these transactions easily, all transactions of the same nature are grouped into one place. This is done by opening accounts in a book called "ledger". So, a ledger is a statement prepared to collect and record transactions re;ating to similar nature or subject into one place. It is a book of secondary entry because it is prepared from journal. When any transactions occur, a recording is made in the journal and then it is re-recorded in the ledger.This process of re-recording is known as posting.
The records of transactions in the journal may run into thousands of pages and it may be difficult to find out the details about a particular transaction. It doesnot provide the information about the details about the position of a particular account. So, to find these transactions easily, all transactions of the same nature are grouped into one place. This is done by opening accounts in a book called "ledger". So, a ledger is a statement prepared to collect and record transactions re;ating to similar nature or subject into one place. It is a book of secondary entry because it is prepared from journal. When any transactions occur, a recording is made in the journal and then it is re-recorded in the ledger.This process of re-recording is known as posting.
Objectives of Ledger
The following are the objectives of ledger:-
1. To provides information about incomes and expenditures- For each head of expenditure and each income, a separate account is opened.It helps to know the amount spent and the incomes on different expenditure and income heads respectively.
2. To provide information about the position of assets and liabilities- A separate ledger account is prepared for the individual asset and liability which helps to know its effect on financial position of business during a particular period.
3. To provide information regarding the purchase and sales- A business firm can have several purchases and sales. A purchase account is prepared to know the total purchase made duriing the period and similarly, sales account is prepared to know the total sales during the period.
4. To help in th preparation of trial balance- Trial balance is prepared on the basis of information provided by the ledger account. So, ledger account is immense help for preparing trial balance.
1. To provides information about incomes and expenditures- For each head of expenditure and each income, a separate account is opened.It helps to know the amount spent and the incomes on different expenditure and income heads respectively.
2. To provide information about the position of assets and liabilities- A separate ledger account is prepared for the individual asset and liability which helps to know its effect on financial position of business during a particular period.
3. To provide information regarding the purchase and sales- A business firm can have several purchases and sales. A purchase account is prepared to know the total purchase made duriing the period and similarly, sales account is prepared to know the total sales during the period.
4. To help in th preparation of trial balance- Trial balance is prepared on the basis of information provided by the ledger account. So, ledger account is immense help for preparing trial balance.
Subsidiary Books
Meaning
There are numerous transactions which occur so many times in a day. It is inadequate and inconvenient to record the transaction in the book of original entry i.e. journal. Every transaction recorded in journal becomes thick, bulky, tedious and consumes more time, labour and money. So the transactions which are of repetitive nature are recorded in a separate book through special journal. Such separate book of original entry, maintained for recording the similar and repetitive types of transactions is known as subsidiary books. Also known as sub-journal or sub- division of journal, this book includes purchase book, sales book, purchase return book, sales return book and cash book.
There are numerous transactions which occur so many times in a day. It is inadequate and inconvenient to record the transaction in the book of original entry i.e. journal. Every transaction recorded in journal becomes thick, bulky, tedious and consumes more time, labour and money. So the transactions which are of repetitive nature are recorded in a separate book through special journal. Such separate book of original entry, maintained for recording the similar and repetitive types of transactions is known as subsidiary books. Also known as sub-journal or sub- division of journal, this book includes purchase book, sales book, purchase return book, sales return book and cash book.
Accounting Basics
Management Accounting
As its name implies, Management (or Managerial) Accounting provides that information which is used by managers within the company. The information provided can be as broad as long range financial projections or as detailed as analyzing cost variances (ie budget overages). Wikipedia defines management accounting as being " concerned with the provisions and use of accounting information to managers within organizations, to provide them with the basis in making informed business decisions that would allow them to be better equipped in their management and control functions."
While management accounting concerns the internal use of information, Financial Accounting concerns the external use of accounting information. Of course financial accounting concepts are used in management accounting. Financial accounting involves providing information which is useful to external users such as prospective buyers and investors, creditors, government agencies, etc. Financial Statements are the most provided piece of information. These include the Balance Sheet and Income Statement (to be explained in a future post). Wikipedia defines financial accounting as "the field of accountancy concerned with the preparation of financial statements for decision makers, such as stockholders, suppliers, banks, government agencies, owners, and other stakeholders. Financial accountancy is used to prepare accounting information for people outside the organization or not involved in the day to day running of the company."
As its name implies, Management (or Managerial) Accounting provides that information which is used by managers within the company. The information provided can be as broad as long range financial projections or as detailed as analyzing cost variances (ie budget overages). Wikipedia defines management accounting as being " concerned with the provisions and use of accounting information to managers within organizations, to provide them with the basis in making informed business decisions that would allow them to be better equipped in their management and control functions."
While management accounting concerns the internal use of information, Financial Accounting concerns the external use of accounting information. Of course financial accounting concepts are used in management accounting. Financial accounting involves providing information which is useful to external users such as prospective buyers and investors, creditors, government agencies, etc. Financial Statements are the most provided piece of information. These include the Balance Sheet and Income Statement (to be explained in a future post). Wikipedia defines financial accounting as "the field of accountancy concerned with the preparation of financial statements for decision makers, such as stockholders, suppliers, banks, government agencies, owners, and other stakeholders. Financial accountancy is used to prepare accounting information for people outside the organization or not involved in the day to day running of the company."
Accounting principle
Accountant Job
Accountant Job
It also recognizes and interacts with devices placed on its surface, so cell phone users can easily buy ringtones or change payment plans by placing their handsets on in-store displays, or a group of people gathered round the table can check out the photos on a digital camera placed on top.
It also recognizes and interacts with devices placed on its surface, so cell phone users can easily buy ringtones or change payment plans by placing their handsets on in-store displays, or a group of people gathered round the table can check out the photos on a digital camera placed on top.
Performance Accounting Basic
Performance Accounting Basic
Almost as common a term as cash nowadays, accounts receivable is an accounting term meaning amounts owed to a business by other business or customers (individuals or otherwise). An accounts receivable arises anytime when goods are sold but cash is not received immediately; thus when you purchase something for cash at Walmart you are not creating an accounts receivable. If you commit to purchase something (say a lawnmower) and you are offered the option to pay next month, now you have created an accounts receivable on the retailers books.
Unlike a note receivable (to be discussed next), there is generally no signed agreement beyond an invoice for an accounts receivable. They are generally short term in nature (less than a year, if not only a couple months). Because of their short term nature, they are generally listed as a current asset on the balance sheet next after cash.
Almost as common a term as cash nowadays, accounts receivable is an accounting term meaning amounts owed to a business by other business or customers (individuals or otherwise). An accounts receivable arises anytime when goods are sold but cash is not received immediately; thus when you purchase something for cash at Walmart you are not creating an accounts receivable. If you commit to purchase something (say a lawnmower) and you are offered the option to pay next month, now you have created an accounts receivable on the retailers books.
Unlike a note receivable (to be discussed next), there is generally no signed agreement beyond an invoice for an accounts receivable. They are generally short term in nature (less than a year, if not only a couple months). Because of their short term nature, they are generally listed as a current asset on the balance sheet next after cash.
Exhaust System
Exhaust System
Searching for best exhaust system on Internet? Did you already find it? I think you already know that internet is best place to find resource of various products and services including exhaust systems and other car accessories. Of course, there are many online stores that have large collections of exhaust systems so you can conveniently buy at the store you like.
Exhaust Systems is very important for the life of the car. As I know that the Exhaust Systems must not be blocked and must be a filters so as not to cause pollution. If you want to have best exhaust system for you car or truck, then only one place at carid.com. They realize your dreams by providing a variety of beautiful models exhaust pipe and safe and can filter pollution well.
Come there then you can see almost all type exhaust system such as Acura Exhaust System, Audi Exhaust System, BMW Exhaust System, Buick Exhaust System, Cadillac Exhaust System, Chevy Exhaust System, Chrysler Exhaust, Dodge Exhaust System, Ford Exhaust System, and more.
You can get much benefit from Carid like the price offered is too low and in accordance with the satisfaction . Beside that, various models and brands available there. Don't worry payment can be done by using visa, master card, paypal and the other more. What you looking for? just go to carid.com and get your exhaust system.
Accounting Basics: Assets
Accounting Basics: Assets
As hinted in my previous entry, the balance sheet is comprised of three basic sections: assets, liabilities and owners equity. Assets are resources or items of value owned by the business. They are items of value which can be used or exchanged in the production or delivery of services of the business.
Typically, the most common asset people think of is cash. Cash can be exchanged to purchase office supplies, raw materials used in production, pay employees, etc.; thus it is an asset of the business. Machinery is another asset; it is used in the production of the goods or services delivered by the business.

Substantial effort is made by accountants in valuing assets; some of which may not have a clear current value. For example, a piece of equipment purchased five years ago for $100,000 and used daily in the operation of the business is not worth $100,000 today (in the same way that a five year old car is not worth the price paid for it when it was new). In this instance, accountants use depreciation to adjust the value of a 'fixed asset' such as this (to be discussed later).
Accounting principle- Accrual Basis
Accounting principle- Accrual Basis
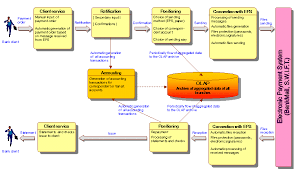
Figures generated / kept in accordance to accounting principle is prepared on accrual basis. For instance, accountant record the provision for warranty ( based on estimate) even though there's no actual cash/ economic outflow yet.In finance, cash basis figures are more relatively more valuable , as compared to accrual basis ( advocated by accounting principle), in order to value a business.What do you think ? You prefer a an accrual method or cash method in valuing a business?
Accounting Basics: The Balance Sheet
Accounting Basics: The Balance Sheet

ne of the fundamental components (for want of a better word) of accounting is the Balance Sheet. The balance sheet is often referred to as a statement of financial position. It can be described as a snapshot that shows the company's financial position at any given moment. Listed in the balance sheet are the company's assets, liabilities and owners equity.
If you view the balance sheet as a two column worksheet, the assets would be in the left column while the liabilities and owners equity would be in the right column. The two columns must be equal.
You won't be able to determine the company's profitability from the balance sheet. What the balance sheet will show is the solvency of the company. Analysts will look at various ratios (i.e. current ratio: current assets / current liabilities) to determine the company's financial well being.
Future entries in my Accounting Basics series will describe each of the components of the balance sheet.
Product Pricing Issues and Strategies
Product Pricing Issues and Strategies


Another good article on BNET (can you tell I like this website). A lot of it is common sense. The helpful thing about the BNET website is how they present the article. It has a very good layout which highlights the main points. This particular article talks about issues and strategies regarding product pricing.


Another good article on BNET (can you tell I like this website). A lot of it is common sense. The helpful thing about the BNET website is how they present the article. It has a very good layout which highlights the main points. This particular article talks about issues and strategies regarding product pricing.
Product Pricing Issues and Strategies
Product Pricing Issues and Strategies


Another good article on BNET (can you tell I like this website). A lot of it is common sense. The helpful thing about the BNET website is how they present the article. It has a very good layout which highlights the main points. This particular article talks about issues and strategies regarding product pricing.


Another good article on BNET (can you tell I like this website). A lot of it is common sense. The helpful thing about the BNET website is how they present the article. It has a very good layout which highlights the main points. This particular article talks about issues and strategies regarding product pricing.
Accounting Basics: Current Assets - Accounts Receivable
Accounting Basics


Almost as common a term as cash nowadays, accounts receivable is an accounting term meaning amounts owed to a business by other business or customers (individuals or otherwise). An accounts receivable arises anytime when goods are sold but cash is not received immediately; thus when you purchase something for cash at Walmart you are not creating an accounts receivable. If you commit to purchase something (say a lawnmower) and you are offered the option to pay next month, now you have created an accounts receivable on the retailers books.
Unlike a note receivable (to be discussed next), there is generally no signed agreement beyond an invoice for an accounts receivable. They are generally short term in nature (less than a year, if not only a couple months). Because of their short term nature, they are generally listed as a current asset on the balance sheet next after cash.


We've previously discussed what Assets are. In an unclassified balance sheet where you only have 3 major classifiations (assets, liabilities and owners equity) that would be in the story. A much more useful report is the Classified Balance Sheet. Here, the three major categories are subdivided to provide readers of the financial statements with much more detailed information. The first such subdivision under assets is Current Assets.
Current Assets are defined as those assets which will either be converted into cash or otherwise 'used up' by the business in a relatively short period of time (generally one year or less). On the balance sheet, they are generally presented in order of liquidity; thus cash is generally listed first.
Other examples of current assets include accounts receivable, notes receivable (which often have a current and a non-current portion) and prepaid expenses. These will be examined in future entries.


Almost as common a term as cash nowadays, accounts receivable is an accounting term meaning amounts owed to a business by other business or customers (individuals or otherwise). An accounts receivable arises anytime when goods are sold but cash is not received immediately; thus when you purchase something for cash at Walmart you are not creating an accounts receivable. If you commit to purchase something (say a lawnmower) and you are offered the option to pay next month, now you have created an accounts receivable on the retailers books.
Unlike a note receivable (to be discussed next), there is generally no signed agreement beyond an invoice for an accounts receivable. They are generally short term in nature (less than a year, if not only a couple months). Because of their short term nature, they are generally listed as a current asset on the balance sheet next after cash.


We've previously discussed what Assets are. In an unclassified balance sheet where you only have 3 major classifiations (assets, liabilities and owners equity) that would be in the story. A much more useful report is the Classified Balance Sheet. Here, the three major categories are subdivided to provide readers of the financial statements with much more detailed information. The first such subdivision under assets is Current Assets.
Current Assets are defined as those assets which will either be converted into cash or otherwise 'used up' by the business in a relatively short period of time (generally one year or less). On the balance sheet, they are generally presented in order of liquidity; thus cash is generally listed first.
Other examples of current assets include accounts receivable, notes receivable (which often have a current and a non-current portion) and prepaid expenses. These will be examined in future entries.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)








